Are ABC cables affecting power distribution in India?
India’s power distribution system is a complex network designed to deliver electricity efficiently across vast distances and varied terrains. In this intricate web, the role of ABC cables (Aerial Bundled Cable) is increasingly significant. As the country seeks to modernize its infrastructure, understanding how ABC cables influence power distribution is critical.
What are ABC Cables?
Overhead Bunching (ABC) is an innovative concept in overhead power distribution. Compared to conventional bare conductor OH distribution systems, ABC cables offers higher safety and reliability, lower power losses, voltage regulation stability, and ultimately system economics, resulting in lower installation, maintenance, and operating costs. The system is ideal for rural power distribution and is especially suitable for installation in difficult terrain such as hilly areas, dense forests, and coastal areas. No trees need to be cut or trimmed to lay this line.
ABC cables are also considered the best choice for power distribution in congested urban areas with narrow driveways. It is convenient to lay it in densely populated areas where narrow gaps between dwellings prevent the laying of bare conductors. It also prevents accidents due to electrocution. The system offers significant advantages in terms of laying costs compared to underground cables. Underground cable installation is more expensive than overhead lines, with a capital cost ratio of up to 20:1. In addition, because it is visible, faults can be detected and corrected easily and quickly. In addition, unlike underground cables, it avoids damage caused by waterlogging.

Construction of ABC cables
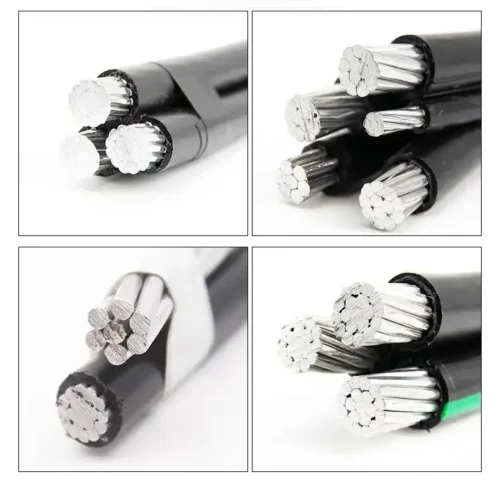
The AB cable consists of aluminum insulated phase wires stranded and wound on bare or insulated wiring harnesses made of aluminum alloy, which are used as a support system and also as a neutral or ground wire. The assembly is suspended directly from distribution poles/towers or building facades using standard hardware. They are available in three basic configurations:
- four core systems
- Insulated Bearing Cord System
- Exposed Loadcord System
The Bureau of Indian Standards has endorsed IS 14255 as the standard for overhead bundled cables. This standard recognizes bundled cables using bare wires and/or insulated bundles. This has led to much confusion as the hardware required for both is different in design and application. In addition, Section 6 of IS 14255:1995 states that standards for commonly used fittings are under consideration and will be published soon. However, no standards have been developed to date.
1) Quad-core systems
Anchor assembly: the entire harness is supported on the pole by anchor clips. All four wires are clamped inside the anchoring assembly and the load of the entire harness is distributed on each wire. The assembly can be secured to the pole with suitable brackets or bolts.
Suspension assembly: Suspension clips are used to secure the entire four-core system bundle to the pole with the help of suspension brackets or hook bolts through the pole.
2) Exposed cable system
Anchor Assembly: In this system, the anchor clip is used to secure only the exposed rigging, not the entire rigging bundle. This assembly is secured to the pole with the help of PCC pole clamps and hooks.
Suspension Assembly: Again, the Suspension Clip is used only to secure the exposed load-bearing wire, which carries the load of the entire bundle. This assembly is secured to the pole using a PCC pole clamp and hook.
3) Insulated Wire System
Anchor assembly: The anchor clamp consists of an aluminum alloy housing and a UV-stabilized thermoplastic inner wedge, which prevents damage to the insulation of the carrier cable. The clamping of the load-bearing cable eliminates the need for other mechanical components. Anchor brackets and stainless steel straps are used to secure the assembly to the pole. The most common standard for anchoring assemblies is NFC 33 041.
Suspension assemblies: Suspension clamps are made of UV-stabilized thermoplastic glass-reinforced material. Specially designed weak links (also known as fuse links) allow for hardware breakage rather than cable breakage. The entire assembly is secured to the pole with suspension brackets and stainless steel straps or bolts. The most common standard for suspension assemblies is NFC 33 040.
Advantages of ABC Cables
1. Enhanced Safety:
The insulated nature of ABC cables reduces the risk of electrical accidents, which is a significant concern in densely populated areas. The insulation prevents live wires from coming into contact with each other, trees, or buildings, thus minimizing the potential for fires or electrical shocks.
2. Reduced Power Loss:
Power loss due to technical issues such as line faults or illegal tapping is a common problem in traditional power distribution systems. ABC cables mitigate these issues by providing better protection against external factors and reducing power theft.
3. Ease of Installation:
ABC cables are easier and quicker to install than traditional overhead lines. Their bundled nature allows for straightforward deployment across various terrains, including urban areas with complex infrastructure.
4. Cost-Effective Maintenance:
The durability and resilience of ABC cables lead to fewer maintenance requirements compared to traditional power lines. The reduced need for frequent repairs translates to lower maintenance costs over time.

How to lay an ABC network
There are two methods of laying an ABC network: a) the layout method and b) the slack tension method.
a) Layout Method
This method is used in the following situations, e.g. crossing roads and single service supply. After ensuring that the ground is free of sharp objects, the entire ABC cable is laid on the ground and its ends are connected to the tow rope. Suspension or anchoring devices are fixed to the intermediate rods and temporary pulleys are suspended from them. Tension the ABC cable until the desired droop is achieved. Then anchor or suspend the cable span by span to each pole span and remove the pulleys and winches.
b) Loose Tension Method
This is the most common method of erecting ABC networks as it is quick and easy. The following steps can be followed:
- Suspension or anchoring devices are fixed to the intermediate poles along with temporary pulleys.
- A haul rope is passed through each pulley. One end of the rope is connected to the ABC cable via a swivel and hauling handle, and the other end is connected to an automatic winch on the ground.
- The winch pulls back the tow rope and then the ABC cable. At the same time, a brake on the cable reel support prevents the ABC cable from sliding back until the cable reaches the end bar. Finally, the ABC cable is anchored or suspended to each pole and the pulleys are removed.
Comparison of slack tension and layout methods
Slack tensioning allows cables to be laid over more spans, whereas the number of spans in the layout method is limited.
The slack method saves time because more time is spent adjusting and securing manual winches or manually lifting cables in the layout method.
The slack method prevents ABC cables from being damaged by sharp edges or objects on the ground during lifting. The sag and tensioning parameters of the cable bundle depend on the ambient temperature, the distance between poles (i.e. span), cable configuration, and weight.
ABC cABLES Connections
Insulation Puncture Connection: The IPC is used to connect the ABC network to the service line. It is the most critical component of an AB line because it establishes electrical continuity without stripping the insulation and can therefore be used on energized lines. The construction allows the joint to be completely sealed against any water intrusion, thus preventing long-term damage to the conductors.
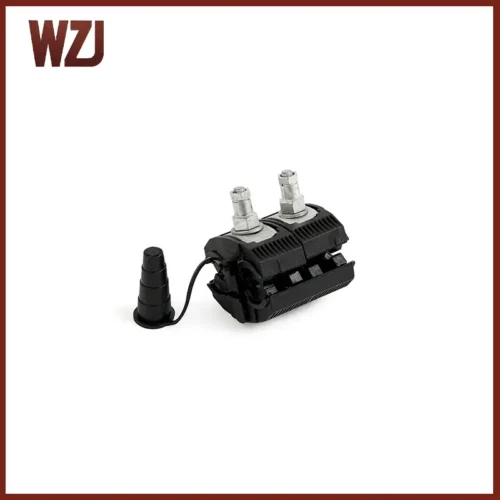
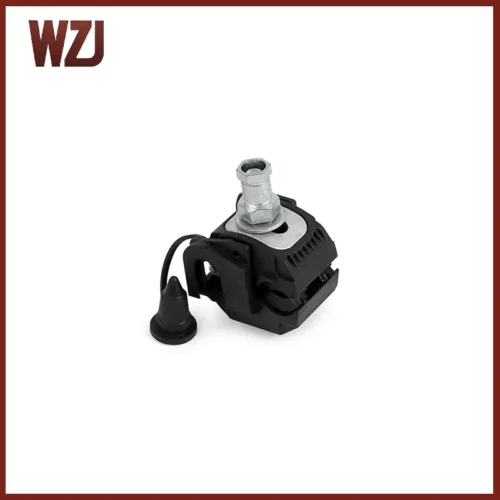



We have a detailed explanation of how to choose an insulated piercing connector in this article over here: THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO INSULATION PIERCING CONNECTOR: 5 TIPS FOR CHOOSING THE BEST
Of course you can contact us directly to help you!
Terminations and connections
Pre-insulated sleeving: Pre-insulated sleeving is used to connect two low-voltage ABCs. It is used for installation, repair, or replacement of connections.
Pre-insulated lugs: Pre-insulated lugs are made of copper palms friction-welded to an aluminum cylinder. It is used to connect the ABC cables to the device terminals. The underwater dielectric strength exceeds 6 KV.
Impact on India’s Power Distribution
Urban Power Distribution
In urban areas, where space is limited and the population density is high, the implementation of ABC cables has revolutionized power distribution. The insulated conductors ensure that power can be transmitted safely and reliably through congested streets and densely packed neighborhoods.
Rural Electrification
India’s push towards rural electrification has seen significant gains with the use of ABC cables. These cables are well-suited for rural areas where traditional power lines are susceptible to damage from weather conditions, animals, and human interference. The robustness of ABC cables ensures a stable and continuous power supply to rural households, thereby supporting rural development initiatives.
Environmental Considerations
The installation of ABC cables has a positive environmental impact. Traditional power lines often require extensive tree trimming or removal to prevent interference, leading to environmental degradation. ABC cables, on the other hand, can be installed with minimal tree cutting, preserving the natural landscape and promoting ecological balance.
Case Studies
Urban Implementation: Mumbai
Mumbai, one of India’s largest metropolitan areas, has successfully integrated ABC cables into its power distribution network. The transition has resulted in fewer power outages, improved safety, and enhanced overall reliability of the electricity supply.
Rural Success: Uttar Pradesh
In Uttar Pradesh, the use of ABC cables in rural electrification projects has led to a significant reduction in power theft and technical losses. The consistent power supply has empowered local communities, facilitating economic growth and improving the quality of life.
Conclusion
Given all these advantages, it is clear that AB cables are best suited for urban and rural areas in India. This fact is recognized by many nodal agencies like Power Grid, REC, and BIS. Several distribution companies in Rajasthan, West Bengal, Orissa, Gujarat, etc. have taken the lead in implementing bundled conductors. The implementation has resulted in a significant reduction in power losses, sometimes by as much as 40%. However, the fragmentation of the initiatives taken has led to unplanned and haphazard development and gross mismatch of product specifications.
Most contractors expressed dissatisfaction with the quality and timely availability of materials, leading to project delays. The lack of coordinated efforts and the absence of a centralized body to oversee these efforts resulted in different SEBs directly aligning product specifications to existing international standards. Let us quickly examine the root cause of these problems.
Traditionally, since we have been working with open wire systems, over some time, all those working with the system have gained a good understanding of what to check during installation. One of the main concepts of an open wire system is that the mechanical strength of the accessories used is equal to or greater than the mechanical strength of the suspension cables. This is a good thing for open-wire systems. For AB cable systems this concept needs to be changed and various standards take this change in concept into account, notably the French standard, who are the main users of this system.
Now, as the cables are insulated, the insulation must be protected by the use of clips supplied with the various accessories. This is the main reason why the standard specifies that the mechanical strength of the accessories used in AB cable systems should be less than the ultimate mechanical strength of the AB cables used.
The logic behind this is that since we can work electrically on AB cables, the AB cables need to be protected from breakage, which can occur if the mechanical strength of the attachment is greater than that of the AB cable. This also proves that a break in the cable means a loss of power to the connected unit and therefore a loss of revenue.
In the French standard, the mechanical strength of the accessory is designed to be weaker, so that if the accessory fails, only the cables fall out from these points and can be re-laid with a new accessory without interruption of power and loss of revenue. As with any product variant, this technology has developed multiple variants in different countries. For all potential users in India, it is critical to understand the ‘nuts and bolts’ of the new technology and adapt it to our regional, technical, and environmental conditions.
Website: https://www.wzjelec.com/
Product: https://wzjelec.com/product
Email: rose@sunjelec.comAuther: Leb